Diabetes: Understanding the Disease and How to Manage It
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people around the world. It is a disease that occurs when the body cannot produce or use insulin properly, which is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is a metabolic disorder that occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough of it.
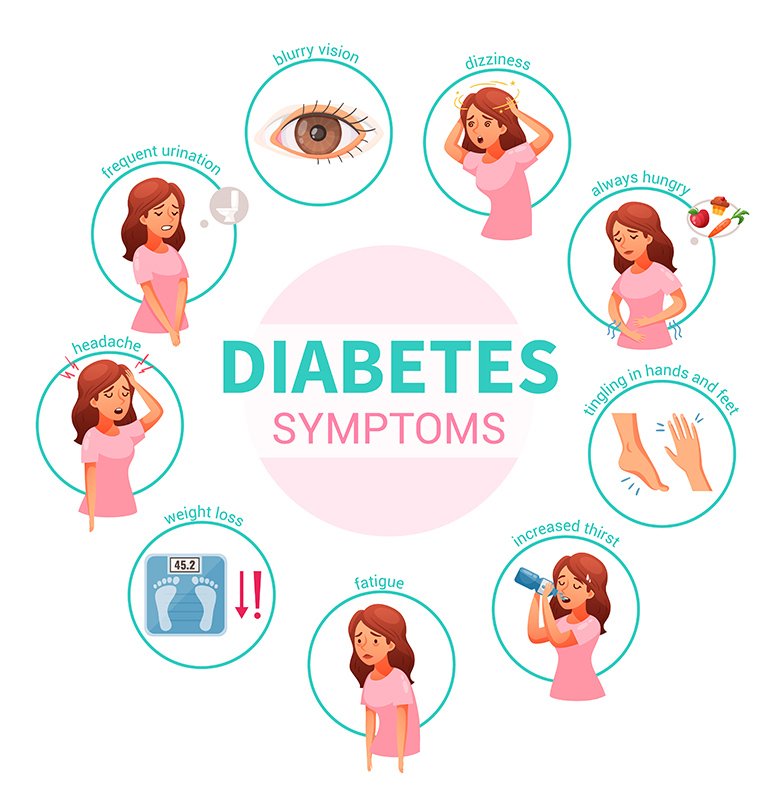
Symptoms of diabetes may include frequent urination, excessive thirst, hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing wounds. If left untreated, diabetes can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and blindness.
While there is no cure for diabetes, it can be managed effectively through a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and monitoring blood sugar levels. Here are some tips for managing diabetes:
Eat a healthy diet:
A healthy diet is an essential part of managing diabetes. Focus on eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-fat foods.
Exercise regularly:
Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, most days of the week.
Monitor blood sugar levels:
Keeping track of your blood sugar levels is important for managing diabetes. Your doctor can advise you on how often you should check your blood sugar levels and what your target range should be.
Take medication as prescribed:
If you have type 1 diabetes, you will need to take insulin injections or use an insulin pump to manage your blood sugar levels. If you have type 2 diabetes, your doctor may prescribe oral medications or insulin injections to help control your blood sugar levels.
Maintain a healthy weight:
Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as well as make it more difficult to manage the disease. Aim for a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
Get regular check-ups:
Regular check-ups with your doctor are important for monitoring your blood sugar levels, managing any complications that may arise, and adjusting your treatment plan as needed.
In conclusion, diabetes is a serious condition that requires ongoing management and care. By making healthy lifestyle choices, monitoring your blood sugar levels, and working closely with your healthcare team, you can effectively manage diabetes and reduce your risk of complications.






Leave a Reply